What Should You Know About an Electrical Wire Cabinet?
13th Feb 2026
Key Highlights
-
Electrical wire cabinets protect, organize, and distribute power and control wiring safely
-
Proper cabinet planning reduces heat buildup, downtime, and inspection issues
-
Industrial electrical cabinet wire management improves accessibility and long-term reliability
-
Running electrical wire through cabinet openings requires protection and compliance awareness
-
Securing electrical wires inside cabinet spaces prevents strain, abrasion, and failure
-
Labeling is critical for compliance, maintenance speed, and workplace safety
-
Durable industrial label printers reduce rework and support audit readiness
Electrical systems rarely fail because of a single component. More often, failures start with poor planning, overcrowded wiring, unclear labeling, or cabinets that were never designed for long term operation. An electrical wire cabinet sits at the center of this risk.
For facility managers, electricians, and industrial teams, the challenge is not just installing wires. It ensures that wiring remains safe, traceable, serviceable, and compliant years after installation. Poor cabinet design leads to overheating, inspection delays, unsafe maintenance conditions, and extended downtime.
This guide is built to solve those problems. It explains what an electrical wire cabinet is, how to plan and wire one correctly, how standards affect cabinet design, and why proper labeling and wire management are essential. You will also learn how professionals secure electrical wires inside cabinet environments and why industrial electrical cabinet wire management directly impacts safety and efficiency.
What Is An Electrical Wire Cabinet?
An electrical wire cabinet is an enclosed housing designed to contain, protect, and organize electrical wiring and components while supporting safe operation and maintenance.
It serves as a controlled environment where power distribution, control logic, and safety devices are installed in a structured and compliant manner.
Electrical wire cabinets are commonly used in:
-
Industrial automation and machinery
-
Manufacturing and processing plants
-
Commercial facilities and utilities
-
Food and beverage production environments
-
Warehousing and logistics operations
Inside a typical electrical wire cabinet, you may find circuit breakers, terminal blocks, relays, contactors, power supplies, PLCs, drives, and communication equipment. These components are mounted and wired to minimize risk while maximizing accessibility.
How Should You Plan and Design an Electrical Wire Cabinet?
Planning determines whether a cabinet remains serviceable for years or becomes a constant source of issues. Design decisions affect heat management, maintenance access, and inspection outcomes.
1. Assessing Power Requirements and Designing the Wiring Layout
Before any wiring begins, power requirements must be clearly defined. This includes voltage levels, current loads, duty cycles, and environmental conditions.
When designing the layout, planners should consider:
-
Continuous vs intermittent loads
-
Cable sizing and voltage drop considerations for HVAC requirements
-
Separation of power and signal wiring
-
Cable sizing and voltage drop
When running electrical wire through cabinet openings, entry points must be protected with bushings, grommets, or strain-relief fittings. This prevents insulation damage and supports compliance.
Good wiring layout reduces troubleshooting time and minimizes installation errors. Proper power assessment and layout planning prevent overheating, reduce rework, and create a logical foundation for safe cabinet operation.
2. Selecting the Right Cabinet Size, Enclosure, and Components
Cabinet size must allow space for wiring, airflow, and future expansion. Overcrowded cabinets trap heat, increasing failure risk.
Key enclosure considerations include:
-
Environmental exposure
-
Required protection level
-
Mounting location
-
Material durability
Selecting the right enclosure rating ensures that internal components are protected from dust, moisture, and contaminants. Correct cabinet sizing and enclosure selection protect components and support safe long-term operation.
3. Organizing and Managing Wires for Safety and Accessibility
Industrial electrical cabinet wire management is essential for safety, serviceability, and efficiency. Organized wiring allows technicians to trace circuits quickly and reduces the risk of accidental disconnections.
Best practices include:
-
Using a wire duct for routing
-
Bundling related circuits
-
Maintaining consistent routing paths
-
Separating high voltage and low voltage wiring
Securing electrical wires inside cabinet environments requires appropriate fastening methods such as clamps, tie mounts, or lacing. Loose wiring leads to abrasion, vibration damage, and airflow obstruction.
Strong wire management improves safety, reduces wear, and speeds maintenance tasks.
4. Ensuring Proper Ventilation, Cooling, and Load Balance
Heat is a major threat to cabinet reliability. Power supplies, drives, and transformers generate continuous heat that must be managed.
Cooling strategies include:
-
Passive ventilation
-
Filtered fan systems
-
Proper component spacing
Load balancing across phases reduces uneven heating and improves electrical stability. Effective cooling and load management protect components and extend the lifespan of the cabinet.
5. Labeling Wires and Components for Easy Identification and Compliance
Labeling is a core requirement for safety and compliance. Clear identification allows technicians to locate circuits quickly, isolate power safely, and perform maintenance without error.
Labeling requirements include:
-
Durable materials that resist heat, oil, vibration, and cleaning chemicals
-
Clear, legible text that remains readable over time
-
Consistent naming for circuits, panels, and components
Accurate labeling reduces downtime, supports inspection compliance, and improves overall workplace safety.
6. Planning for Future Expansion, Maintenance, and Upgrades
Electrical systems change over time. Cabinets should be designed with spare capacity and clear documentation.
Planning ahead includes:
-
Leaving space for additional wiring
-
Maintaining spare terminal positions
-
Keeping labeling and drawings aligned
Future-ready cabinet design reduces upgrade costs and minimizes disruption.
What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining an Electrical Wire Cabinet?
Maintenance ensures long term safety and reliability by preventing overheating, loose connections, and labeling issues. Regular inspections, cleaning, and documentation updates help reduce downtime, support compliance, and extend the service life of electrical wire cabinets.
1. Perform Regular Inspections and Cleaning
Regular inspections are the first line of defense against electrical cabinet failures. Dust, debris, and residue can accumulate quickly inside an electrical wire cabinet, especially in industrial or high-traffic environments. Over time, this buildup restricts airflow, traps heat, and accelerates component wear.
Inspections should focus on identifying loose wiring, damaged drywall insulation, discoloration from overheating, corrosion on terminals, and blocked ventilation paths. Cleaning should be done using non-conductive tools and approved methods to avoid introducing moisture or static discharge. High-dust environments may require more frequent inspection cycles.
A consistent inspection routine helps detect minor issues before they escalate into shutdowns, safety incidents, or failed inspections.
2. Tighten and Test Electrical Connections
Electrical connections loosen gradually due to vibration, load changes, and thermal cycling. Even a slightly loose terminal can create resistance, leading to localized heating and eventual failure.
Testing and tightening connections should be part of scheduled maintenance. This includes checking terminal blocks, breakers, grounding points, and high-load connections. Torque values should follow manufacturer specifications to avoid over-tightening, which can damage conductors or terminals.
Thermal imaging and electrical testing can help identify problem areas that are not visible during visual inspections. Addressing loose connections early prevents arc faults, overheating, and unplanned downtime.
3. Keep Labels and Documentation Updated
Labels and documentation are only effective if they reflect the current cabinet configuration. Any modification, repair, or expansion should trigger an update to wire labels, terminal identifiers, and electrical drawings.
Outdated labels create confusion during maintenance, increase the risk of isolating the wrong circuit, and slow troubleshooting. In regulated environments, incorrect labeling can also lead to inspection failures.
Best practice includes verifying label accuracy during maintenance checks and ensuring that cabinet documentation, schematics, and panel schedules match the physical layout. Using durable, clearly printed labels helps ensure information remains legible over time.
4. Monitor Temperature and Airflow
Temperature monitoring provides early warning of electrical stress inside a cabinet. Excess heat is one of the most common causes of component failure and insulation breakdown.
Monitoring should include checking ambient cabinet temperature, identifying hot spots, and ensuring airflow paths remain unobstructed. Fan operation, filter condition, and vent placement should be reviewed regularly, especially in cabinets with high power density.
Changes in temperature trends often indicate underlying issues such as overloaded circuits, failing fans, or blocked ventilation. Addressing these issues early prevents component damage and extends cabinet service life.
5. Schedule Preventive Maintenance and Record Findings
Preventive maintenance brings structure and accountability to electrical cabinet care. Rather than reacting to failures, scheduled maintenance ensures issues are identified and resolved systematically.
Maintenance schedules should be based on cabinet usage, environmental exposure, and system criticality. Each inspection or service activity should be documented, including findings, corrective actions, and follow-up requirements.
Maintenance records support audits, demonstrate compliance, and help identify recurring problems or trends. Over time, this data allows teams to refine maintenance intervals and improve overall system reliability.
What Standards Govern Electrical Wire Cabinets?
Electrical wire cabinets are governed by multiple safety, construction, and compliance standards. These standards exist to reduce electrical hazards, protect workers, and ensure cabinets remain safe and serviceable throughout their operating life. Understanding how each standard applies helps avoid inspection failures, redesign costs, and operational risk.
Below are the most relevant standards influencing electrical wire cabinet design, wiring, labeling, and maintenance.
1. National Electrical Code (NEC)
The National Electrical Code (NEC) establishes minimum safety requirements for electrical installations in the United States and is widely referenced in North America. It defines how wiring must be installed, protected, grounded, and routed within enclosures.
For electrical wire cabinets, the NEC covers critical areas such as conductor sizing, overcurrent protection, grounding methods, and spacing between live parts. It also provides guidance on running electrical wire through cabinet openings, including requirements for abrasion protection, strain relief, and securing conductors to prevent movement.
2. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develops global standards for electrical and electronic systems. IEC standards are especially relevant for manufacturers and facilities operating across multiple regions or exporting equipment internationally.
IEC guidelines influence cabinet design by defining component spacing, insulation requirements, voltage classifications, and safety labeling practices. Many control panels and electrical wire cabinets are designed to meet both NEC and IEC requirements to support broader market acceptance.
3. UL 508A for Industrial Control Panels
UL 508A is a critical standard governing the construction of industrial control panels. It applies directly to electrical wire cabinets used in machinery, automation, and industrial systems.
This standard addresses enclosure construction, component spacing, wiring methods, grounding, attachments, and labeling. UL 508A also defines how components must be secured and identified, which directly impacts industrial electrical cabinet wire management and labeling practices.
4. NEMA Enclosure Ratings
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) defines enclosure ratings that specify how well a cabinet protects internal components from environmental conditions.
NEMA ratings classify enclosures based on resistance to dust, water, oil, corrosion, and physical contact. Selecting the correct NEMA rating is essential for ensuring that an electrical wire cabinet performs reliably in its intended environment.
5. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Regulations
OSHA regulations focus on protecting workers from electrical hazards in the workplace. While OSHA does not replace electrical codes, it enforces safe work practices and requires employers to maintain hazard-free environments.
For electrical wire cabinets, OSHA emphasizes clear labeling, safe access, lockout procedures, and protection against accidental contact with live parts. Cabinets that are poorly labeled or difficult to service safely may violate OSHA requirements.
6. NFPA 70E Electrical Safety in the Workplace
NFPA 70E provides guidance on electrical safety practices, particularly regarding arc-flash hazards and energized work conditions.
This standard influences cabinet labeling by requiring warning labels, voltage identification, and hazard communication. NFPA 70E also emphasizes clear access, proper spacing, and accurate documentation to support safe maintenance procedures.
7. ISO 9001 Quality Standards
ISO 9001 focuses on quality management systems and process consistency. While not an electrical code, it strongly influences how electrical wire cabinets are documented, labeled, and maintained.
ISO standards encourage standardized procedures, accurate records, and continuous improvement. In practice, this means consistent labeling formats, updated documentation, and traceable maintenance records.
8. Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Certification
The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) sets electrical safety standards for equipment installed in Canada. CSA certification is mandatory for many electrical installations and is closely scrutinized during inspections.
CSA standards influence cabinet construction, wiring methods, grounding, and labeling practices. Electrical wire cabinets installed in Canadian facilities must meet CSA requirements to pass inspection and remain legally compliant.
9. CE Marking for European Compliance
CE marking indicates that electrical equipment meets European Union safety, health, and environmental requirements. While not required in Canada, CE marking is relevant for manufacturers exporting cabinets or machinery to European markets.
CE compliance affects cabinet design, labeling, and documentation. It often requires alignment with IEC standards and additional conformity assessments.
Understanding the standards that govern electrical wire cabinets helps ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and smoother inspections. Aligning cabinet design, wiring, labeling, and documentation with these standards reduces risk, prevents costly rework, and supports long term operational reliability.
How Should You Label Wires and Components Inside an Electrical Cabinet?
Electrical cabinet labeling should be clear, durable, and standardized to support safety, compliance, and efficient maintenance. Proper labeling enables technicians to quickly identify circuits, safely isolate power, and meet inspection requirements without guesswork or unnecessary downtime.
Labeling is not a finishing step. It is a core part of electrical cabinet design that directly impacts long term reliability and workplace safety.
-
Selecting the Right Labeling Materials, Methods, and Color Codes: The first step in effective labeling is choosing materials that can survive the cabinet’s operating environment. Electrical cabinets are often exposed to heat, oil, vibration, dust, cleaning chemicals, and occasional moisture. Labels that are not designed for these conditions will fade, peel, or become unreadable over time.
-
Using Clear, Durable, and Standardized Print Formats: Even the best label material fails if the print format is unclear. Labels must be readable without strain, even in low light or crowded cabinet layouts. Small fonts, poor contrast, or inconsistent formatting increase the risk of misinterpretation during maintenance or emergency work.
-
Labeling Both Ends of Wires With Circuit Numbers and Functions: Labeling both ends of every wire is one of the most important yet commonly overlooked practices in electrical cabinet design. Single-end labeling forces technicians to trace wires physically, increasing time and the risk of disturbing adjacent connections.
-
Applying Self-Laminating or Heat-Shrink Labels for Longevity: Environmental exposure is one of the main reasons labels fail inside electrical cabinets. Self-laminating and heat-shrink labels are designed specifically to address this issue.
-
Labeling Terminal Blocks, Relays, and Breakers Consistently and Clearly: Wires are not the only elements that require labeling. Terminal blocks, relays, breakers, contactors, and control devices must also be clearly identified to support safe operation and maintenance.
-
Ensuring Visibility, Organization, and Accurate Documentation: Label visibility is just as important as label content. Labels should be positioned so they can be read without moving wires, opening wire duct covers unnecessarily, or removing components. Poor placement negates the benefits of even the most durable labels.
What Common Labeling Mistakes Should You Avoid in Electrical Wire Cabinets?
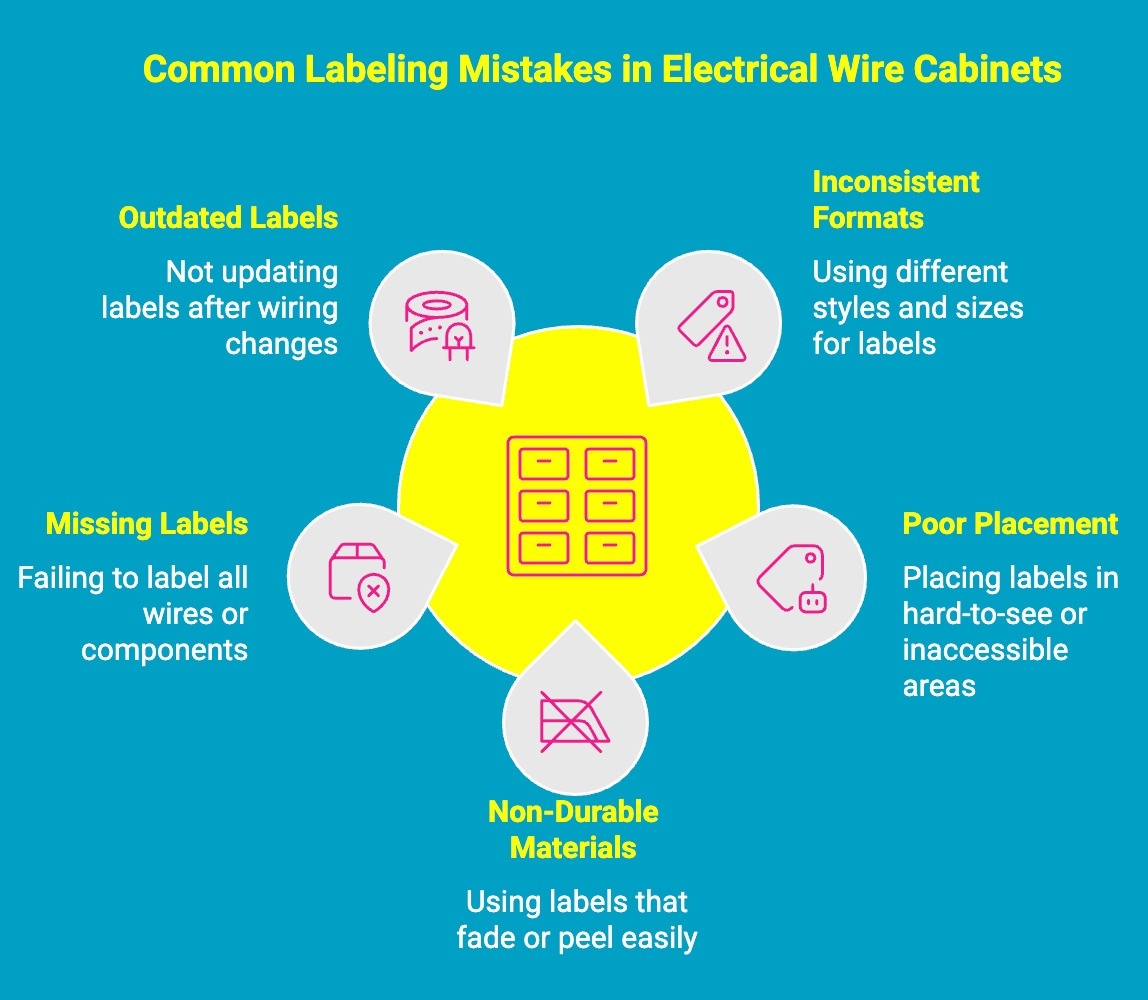
Labeling mistakes reduce safety, slow maintenance, and increase the risk of inspection failures. Avoiding common errors such as inconsistent formats, poor placement, and outdated information ensures electrical wire cabinets remain easy to service, compliant with standards, and safe for technicians working under time pressure.
1. Inconsistent Labeling Formats
Using different fonts, numbering styles, or abbreviations within the same electrical wire cabinet creates confusion. Technicians may misinterpret circuit identifiers or assume wires serve different functions. Consistent formats across all wires and components improve clarity, speed troubleshooting, and reduce human error.
2. Poor Label Placement
Labels that are hidden behind wire bundles, placed inside ducting, or positioned where they cannot be read without moving conductors lose their purpose. Labels should be clearly visible at normal viewing angles to allow safe identification during inspections and maintenance work.
3. Using Non-Durable Label Materials
Labels made from paper or low-grade materials degrade quickly when exposed to heat, oil, vibration, or cleaning chemicals. As labels fade or peel, critical information is lost. Industrial-grade, heat-resistant materials ensure long-term legibility and compliance.
4. Missing or Incomplete Labels
Unlabeled wires, terminals, or breakers force technicians to trace circuits manually, increasing downtime and the risk of mistakes. Every wire and component should include complete identification, such as circuit number, function, or destination, to support safe servicing.
5. Failing to Update Labels After Changes
Electrical cabinets evolve over time. When modifications are made but labels are not updated, information becomes unreliable. Outdated labels increase the risk of isolating the wrong circuit and can lead to failed inspections or unsafe maintenance conditions.
Why Is the MAX LETATWIN LM-550A3BH the Best Printer for Durable Electrical Cabinet Labels?
Electrical wire cabinets require labels that remain legible under heat, oil, vibration, and frequent handling. The MAX LETATWIN LM-550A3BH, available from DuraFast, is purpose-built for electrical and industrial labeling where durability and consistency are critical.
It prints directly onto heat-shrink tubing and wrap-around wire labels, making it ideal for securing electrical wires in cabinet environments and supporting long-term industrial electrical cabinet wire management with PVC options. Labels stay fixed, readable, and compliant even in demanding conditions.
By sourcing the MAX LETATWIN LM-550A3BH and compatible label materials from DuraFast, teams standardize labeling, reduce rework, and stay inspection-ready across all electrical wire cabinets.
Connect with the DuraFast team today to discuss your labeling needs, request product guidance, or explore tailored solutions for your electrical and industrial applications.
Conclusion
Electrical wire cabinets are foundational to safe and reliable electrical systems. From design and wire management to labeling and maintenance, every decision affects performance and safety.
If you are planning a new cabinet or upgrading an existing one, start by reviewing your layout, labeling strategy, and compliance readiness. Invest in durable materials, consistent processes, and tools designed for industrial environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the NEC code for running electrical wire through cabinets?
NEC guidelines require electrical wires to be properly supported, protected at entry points, and sized correctly when running through cabinets. These rules prevent insulation damage, overheating, and mechanical stress that could lead to electrical faults or fire hazards.
Do I need to protect electrical wires when running them inside kitchen cabinets?
Yes. Electrical wires inside kitchen cabinets must be protected from physical damage, moisture, and heat. Local electrical codes typically require approved wiring methods, proper securing, and, in some cases, conduit to ensure safety and inspection compliance.
Is it safe to have exposed electrical wiring inside a cabinet?
No. Exposed electrical wiring increases the risk of electric shock, short circuits, and fire hazards. Most electrical codes require wiring to be enclosed, secured, and protected, and exposed conductors often result in failed safety inspections.
How can I manage and organize cables neatly inside control cabinets?
Use wire duct, cable ties, and tie mounts to route cables along defined paths. Separate power and control wiring, maintain proper bend radius, and label both ends to improve visibility, airflow, and long-term maintenance efficiency.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when running wire under base cabinets?
Common mistakes include leaving wires unsecured, failing to protect them from abrasion, routing near heat or moisture, and skipping conduit where required. These errors increase the risk of damage and often result in failed electrical inspections.
Is it better to rough in electrical wiring before installing cabinets, or after?
Electrical wiring is typically roughed in before cabinets are installed to ensure proper routing, securing, and protection. This approach reduces modification work, improves safety, and makes it easier to meet electrical code and inspection requirements.
What tools or materials are required to route electrical wire through cabinet walls?
Common tools and materials include drill bits, protective bushings, grommets, conduit fittings, cable clamps, and approved fasteners. These components help protect wire insulation, prevent strain, and ensure safe, code-compliant routing.
