Thermal Transfer Printer vs Laser Printer: Key Differences
2nd Feb 2026
Key Highlights
-
Thermal transfer uses heat to melt ribbon ink onto labels; laser uses heat plus pressure to fuse toner powder onto paper.
-
Thermal prints last longer and resist heat, chemicals, and moisture; laser prints can fade or smudge.
-
Thermal can print on paper, polyester, vinyl, and synthetics; laser is mostly limited to paper-based labels.
-
Thermal needs simple ribbon changes; laser needs toner, drum, and fuser replacements.
-
Thermal is best for industrial labels, barcodes, and asset tags; laser is preferred for office docs and short-term labels.
-
Thermal costs more upfront but is cheaper long-term; laser is cheaper to buy but costlier to run over time.
Printers may look similar on the outside, but what’s inside makes all the difference. The choice between a thermal transfer printer and a laser printer isn’t just about technology; it’s about print quality, durability, and long-term value.
While both can produce sharp, professional results, they work in completely different ways. Knowing how they differ can help you pick the right one for your specific printing needs.
In this guide, we’ll compare thermal transfer printers vs laser printers, so you can make a confident, informed choice that delivers the results you expect.
What Is a Thermal Transfer Printer and How Does It Work?
A thermal transfer printer creates an image by using a thermal print head to apply heat to an ink ribbon. As the ribbon and your chosen media pass under the printhead together, the heat melts the ink from the ribbon and transfers it directly onto the surface. This printing process creates a dense, high-resolution image that is extremely durable. Unlike other methods, the image is bonded to the material, not absorbed into it.
The ink ribbons used in thermal transfer printing come in wax, resin, or mixed formulations, and this choice directly impacts how long your print will last and where it can be used.
Wax ribbons are ideal for everyday labels that do not face rough handling, such as shipping labels or warehouse pick lists. Resin ribbons bond much harder to the surface and can survive chemicals, abrasion, UV exposure, and extreme temperatures, making them suitable for compliance labels, outdoor barcodes, industrial asset tags, and safety identification.
In simple terms, you are not just picking a ribbon; you are deciding how durable your printed data needs to be in the real world.
What are the Top Thermal Transfer Printers in 2025?
Choosing the right thermal transfer printer in 2025 comes down to print quality, durability, and how well the device fits your workflow. Below are some of the top models in the market today, from compact desktop units to heavy-duty industrial systems, so you can quickly see which one aligns best with your labeling needs:
1. Godex G500 4" Thermal Transfer Barcode Printer
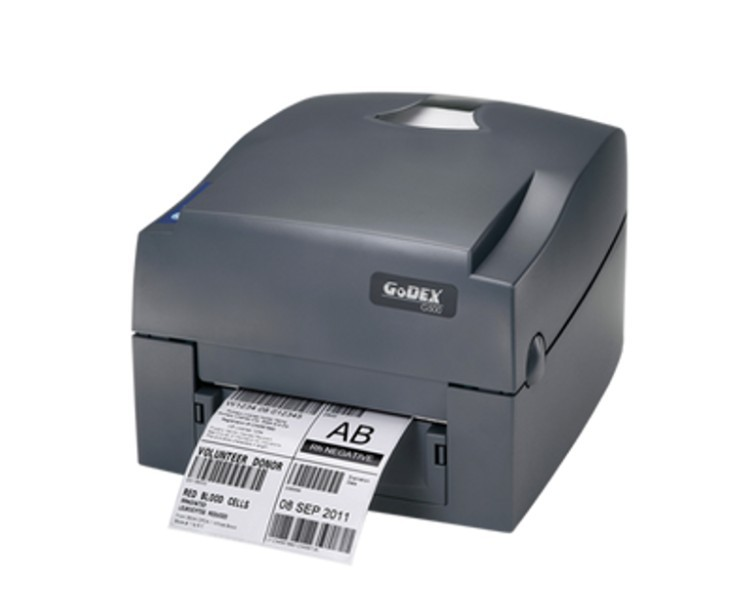

The GoDEX G500 is a 4-inch wide thermal transfer/ direct thermal desktop barcode printer. It supports up to 203 dpi (with optional 300 dpi) resolution, print speeds up to 4-5 ips, and is designed for a variety of label tasks in retail, logistics, or light manufacturing.
Why Businesses Love the GoDEX G500?
-
Compact but versatile desktop unit with both thermal transfer and direct thermal modes.
-
Supports 300 m ribbon length for higher output before reloading.
-
Broad connectivity options (USB, serial, Ethernet) and built for reliable long-term use.
2. Zebra ZD411t 2" Wide 300 dpi, 4 ips Thermal Transfer Label Printer USB/BTLE5
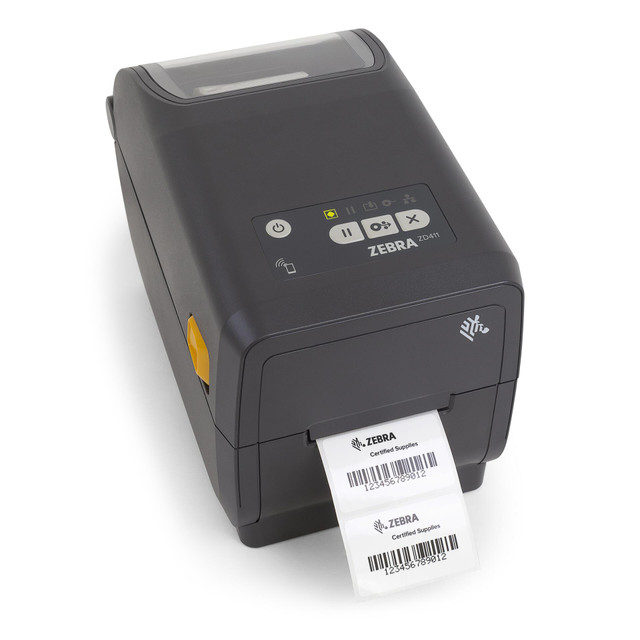

The Zebra ZD411T is a compact 2-inch thermal transfer (and direct thermal) desktop label printer supporting 203/300 dpi resolution. Despite its small footprint, it offers full desktop printer functionality, flexible media handling, and strong connectivity options, including USB, USB Host, Bluetooth LE, and optional WiFi.
Why Businesses Love the Zebra ZD411T?
-
Delivers professional print quality (up to 300 dpi) in constrained spaces.
-
Field-upgradeable connectivity (wireless, Ethernet) and advanced software/management via Zebra’s Print DNA suite.
-
Simplified media loading with intuitive design (color-coded touchpoints) to reduce user error and downtime.
3. SATO WWCLP2001 CL4NX Plus Thermal Transfer Industrial Printer
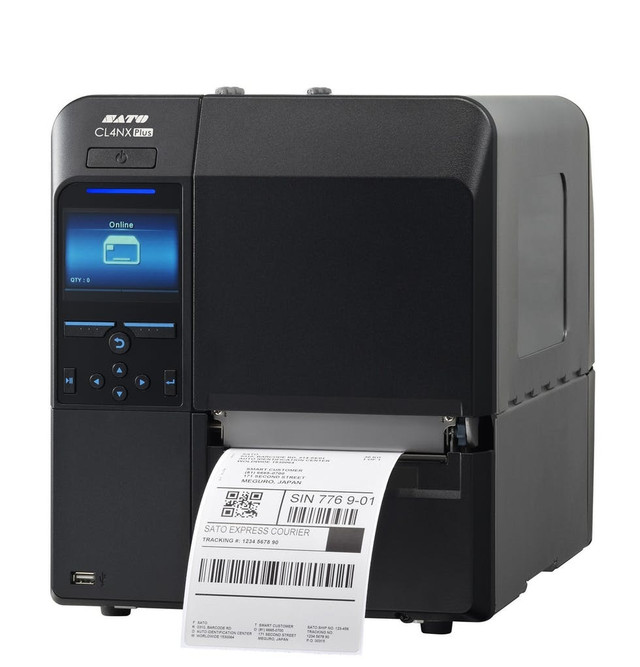

The SATO CL4NX Plus is an industrial-grade 4-inch thermal transfer printer developed for demanding environments. It offers high print precision, speed, and supports both barcode and RFID applications, suitable for manufacturing, logistics, automotive, food, and health industries.
Why Businesses Love the SATO CL4NX Plus?
-
Built for high-demand industrial workflows, able to handle small micro-labels (e.g., PCBs) as well as standard sizes.
-
RFID capable, enabling track-and-trace, asset tagging, and advanced labeling scenarios beyond typical barcode printing.
-
Designed to reduce waste, integrate seamlessly into existing workflows, and deliver efficiency in tough environments.
4. Printronix T6000e 6-Inch Wide 203 dpi T6206 Thermal Transfer Printer
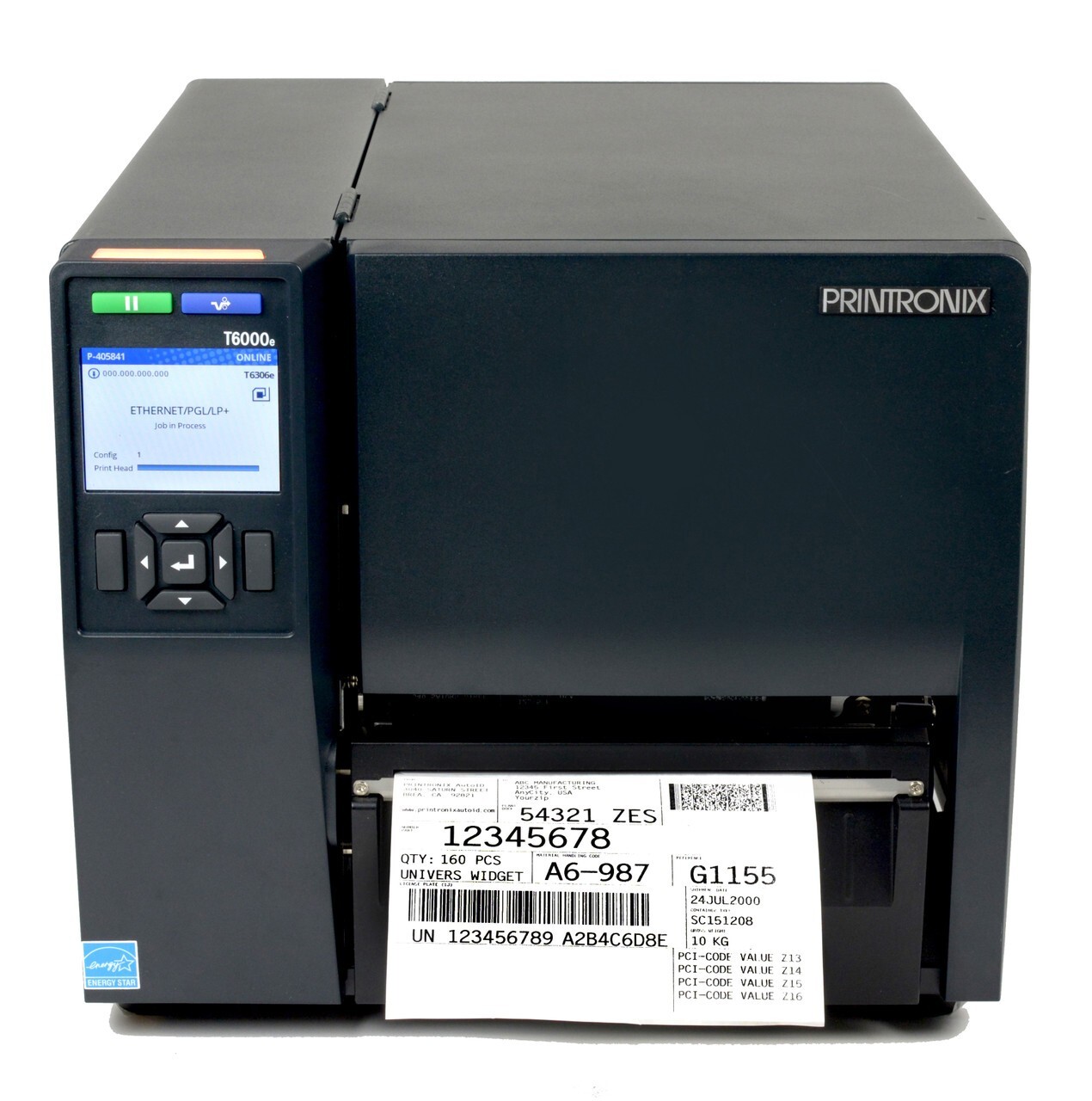

The Printronix T6000e Series is a 6-inch wide enterprise-industrial thermal transfer printer designed for heavy-duty use, with support for large media widths and RFID printing. It targets high-volume operations, label manufacturing, logistics, and other industrial applications needing wide format and advanced connectivity.
Why Businesses Love the Printronix T6000e?
-
Large 6-inch print width supports wide labels, making it suitable for pallet labels, large asset tags, and packaging.
-
RFID printing built in: integrates barcode + RFID workflows in one device, reducing complexity and equipment count.
-
Enterprise-class build means it’s engineered for high volume, continuous operation, and demanding industrial settings.
5. Honeywell PD45S/PD45 Industrial Printer
The Honeywell PD45S/PD45 is an industrial-grade thermal transfer printer positioned for manufacturing, retail, logistics, healthcare, and government applications. It offers rugged build, advanced features, and fits into environments where durability and broad application support matter.
Why Businesses Love the Honeywell PD45?
-
Rugged industrial design suitable for harsh environments, enabling use across manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, retail & government.
-
Alternative to competing printers in the market with Honeywell’s ecosystem and platform support, offering strong longevity and integration.
-
Built to handle heavy-duty label printing workflows — supporting broad media types, heavy volumes, and complex labeling tasks.
What Is a Laser Printer and What Makes It Different?
A laser printer operates quite differently from a thermal printer. It uses laser technology to create an electrostatic image on a rotating component called a print drum. This charged image attracts a powdered ink called toner from its cartridges. The paper then passes the drum, picking up the toner in the shape of your text or image, and a fuser unit applies heat and pressure to permanently bond it to the paper.
Because of this process, laser printers are particularly strong in document printing. The precision of the laser and the fusing method produce sharp, high-resolution output, typically in the 600 to 1200 DPI range, which is ideal for reports, marketing materials, and detailed images. They also handle large print jobs efficiently and often include useful office features like double-sided printing.
Want more information on how laser label printers work? Check out this guide on Everything You Need to Know About a Laser Label Printer.
What are the Top Laser Printers in 2025?
Laser label printers combine speed, precision, and support for specialty media, ideal for businesses looking to print high volumes, use white toner, or achieve premium finishes. Below are five best-in-class models ready for serious label production.
1. Primera LX3000 Color Label Printer - Pigment Ink
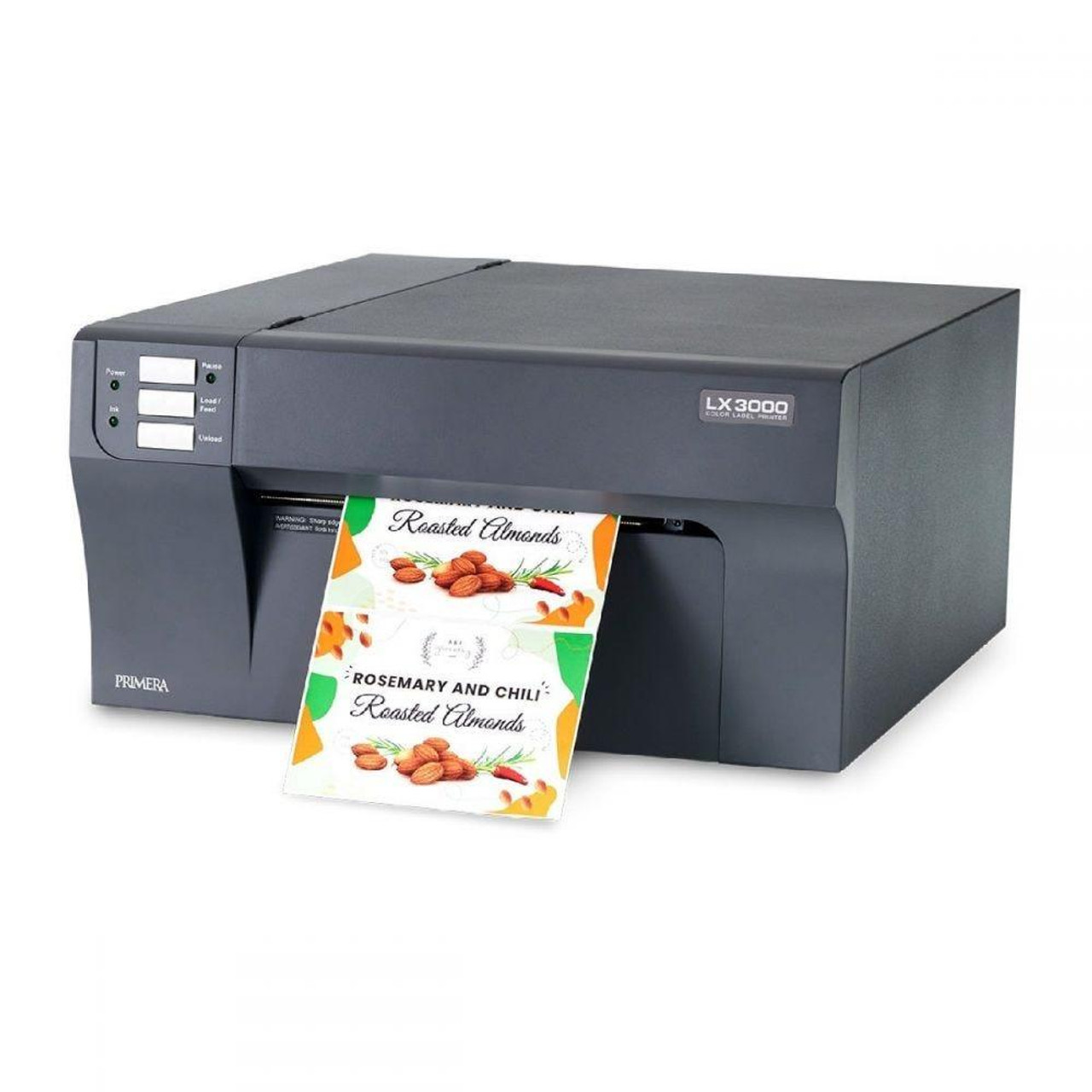

The Primera LX3000 is a desktop colour label printer offering up to 4,800 dpi resolution and printing speeds of around 4.5 ips with a maximum print width of 8.25″. It features a “Big-Ink” system with large pigment ink tanks and a reusable print head, making it suitable for print volumes up to ~7,500 labels per day.
Why Businesses Love the Primera LX3000?
-
Delivers photo-quality full-colour labels in-house rather than outsourcing.
-
Keeps per-label ink cost low due to the large ink tanks and reusable print head.
-
Supports different media types (paper + synthetics) so it can be used across product types (cosmetics, food & beverage, distilleries).
2. Afinia L701 Inkjet Color Label Printer
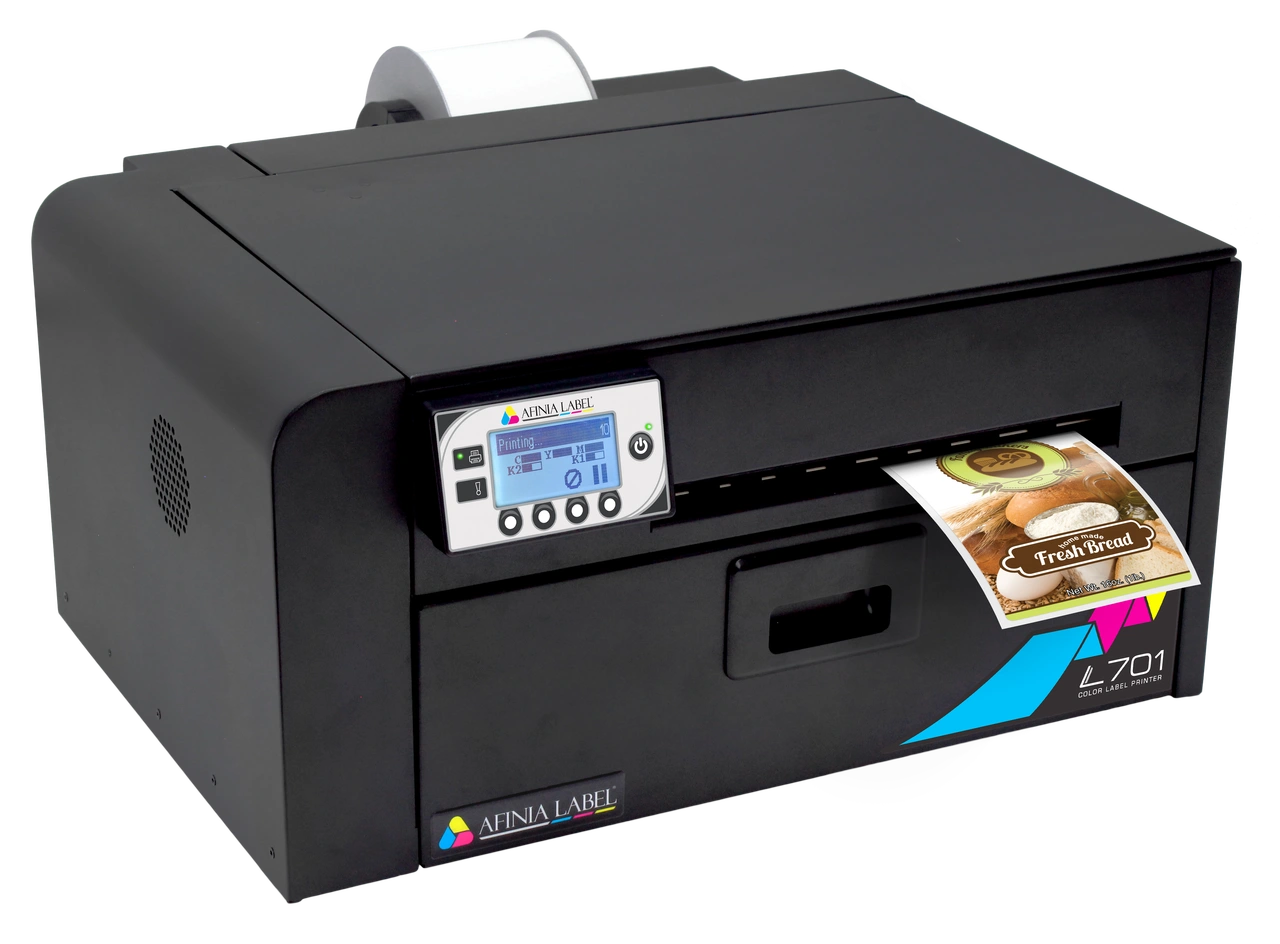

The Afinia L701 is a mid-volume digital colour label printer powered by Memjet™ “waterfall” print-head technology. It offers resolutions up to 1,600×1,600 dpi, a print width of 8.5″ (216 mm), and print speeds up to roughly 6-8″ per second. It includes large 150–200 mL CYMKK ink cartridges and supports a wide range of media, including paper, polyester, polypropylene, and vinyl.
Why Businesses Love the Afinia L701?
-
Affordable entry into full-colour in-house label printing thanks to lower initial cost than many high-end alternatives.
-
Excellent image quality and versatile media compatibility enable crisp branding across multiple product lines.
-
Ideal for small to mid-sized businesses that want to bring colour label production in-house rather than depend on external print runs.
3. Afinia LT5C CMYK + White Color Laser Printer For Labels and Digital Label Press
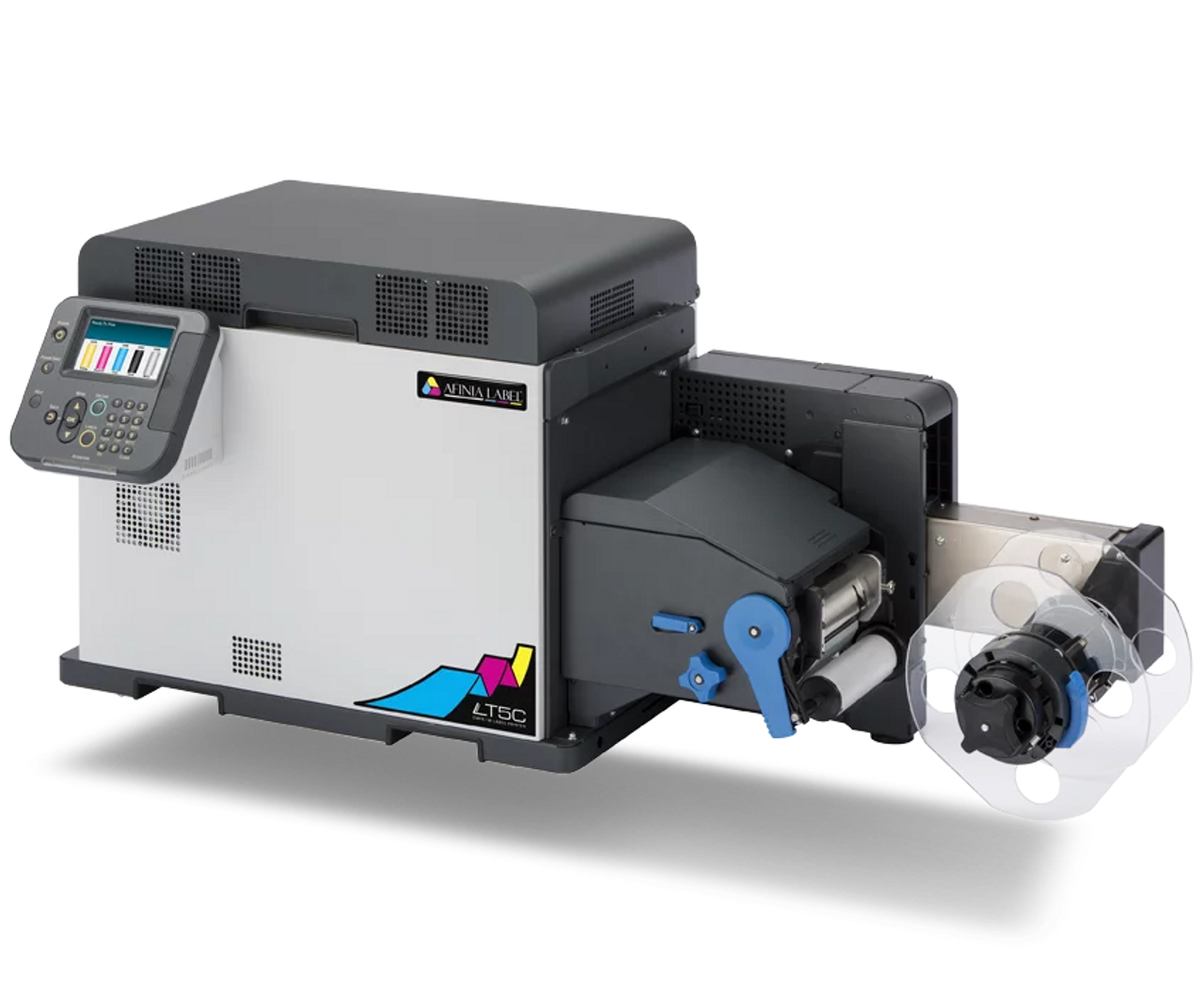

The Afinia LT5C is a laser-based colour label printer offering CMYK plus white toner capability, making it suitable for labels that require white ink (for dark substrates) or specialised packaging. It is positioned for digital label press applications and supports roll-to-roll workflows.
Why Businesses Love Afinia LT5C?
-
Enables printing white ink as well as full colour, unlocking printing on dark or transparent materials (important for premium packaging).
-
Laser technology provides sharp text, graphics, and fine details suitable for higher-end label or packaging production.
-
Supports roll-to-roll setups, making it viable for semi-industrial label production without full-scale press investment.
4. NeuraLabel Sirius Label Printer
The NeuraLabel Sirius Label Printer uses white toner technology to print labels, including white ink output (for dark/clear substrates) in a tabletop format. It is designed to enable premium label production, especially for short runs or specialty applications.
Why Businesses Love NeuraLabel Sirius?
-
Offers white ink capability in a desk-friendly form factor, giving small operations access to premium label styles (metallics, dark backgrounds) without large equipment.
-
Flexible production capability supports niche or premium labelling jobs (limited editions, retail labels) in-house.
-
Helps differentiate packaging or labels through design possibilities (white ink layering, special substrates) that many standard printers cannot handle.
5. AstroNova QL-300 Five-Colour Label Printer
The AstroNova QL-300 is a five-colour label printer designed for label printers who need multiple spot colours in addition to CMYK, allowing extended colour gamut and stronger brand fidelity. It supports media widths and workflows common in professional label production environments.
Why Businesses Love the AstroNova QL-300?
-
Enables printing beyond standard four-colour CMYK by adding spot or specialty colours, helping maintain brand colour accuracy and richer graphics.
-
Suited to label converters or brands requiring premium labels (e.g., craft beverages, specialty foods) who want to control their label production in-house.
-
Supports production workflows for colour-intensive labels, offering an alternative to outsourcing while retaining quality and flexibility.
Thermal Transfer Printer vs Laser Printer: What’s the Main Difference?
The main difference between a thermal transfer printer and a laser printer lies in how they print, the durability of their output, and the type of materials they support. While both deliver sharp, professional-quality prints, they serve very different purposes. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how they compare across key aspects.
1. Printing Method
A thermal transfer printer uses heat to transfer ink from a ribbon directly onto the label material. This creates durable, high-contrast prints that don’t smudge or fade easily. A laser printer, on the other hand, uses a laser beam to form an image with toner powder, which is then fused to the paper’s surface using heat and pressure.
2. Print Durability
Thermal transfer prints are highly durable. They resist heat, moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure, making them ideal for long-term or outdoor use. Laser prints, while crisp and professional, are more prone to smudging, scratching, and fading when exposed to harsh environments.
3. Material Compatibility
Thermal transfer printers can print on a wide range of materials, including paper, polyester, vinyl, and synthetic labels. This versatility makes them suitable for labeling in industrial or specialized applications. Laser printers are limited to paper-based labels and standard office media, restricting their use in environments that require durable or flexible label materials.
4. Maintenance
Thermal transfer printers require minimal maintenance. Only periodic ribbon replacements are needed to keep them running smoothly. Laser printers have a moderate maintenance requirement, involving the replacement of toner cartridges, imaging drums, and sometimes fusers.
5. Ideal For
Thermal transfer printers are best suited for industrial labeling, barcodes, wire markers, and asset tags where long-term readability is essential. Laser printers are ideal for office printing, reports, forms, and short-term labeling tasks that demand speed and sharp text output.
6. Output Type
Thermal transfer printers produce durable, fade-resistant, and long-lasting prints designed for functionality and endurance. Laser printers deliver high-speed, high-volume prints with a polished, professional finish. They are perfect for everyday document needs.
7. Cost Considerations
Thermal transfer printers typically have a higher upfront cost but lower long-term expenses due to their durability and reliability. The consumables (ribbons and labels) are affordable and long-lasting. Laser printers are generally cheaper to buy initially, but the ongoing cost of toner, drums, and maintenance can add up, especially in high-volume printing environments.
Here is a summary of all the key differences between the two types of printers:
|
Category |
Thermal Transfer Printer |
Laser Printer |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Printing Method |
Uses heat to melt ink from a ribbon directly into the label surface for durable, high-contrast prints |
Uses a laser to create an electrostatic image, then fuses toner powder onto paper with heat and pressure |
|
2. Print Durability |
Extremely durable. It can resist heat, moisture, chemicals, and UV. This is ideal for long-term/outdoor use |
Crisp output but more prone to smudging, scratching, and fading in harsh environments |
|
3. Material Compatibility |
Works with paper, polyester, vinyl, and synthetics. This makes it suitable for industrial and specialty applications |
Mostly limited to paper-based labels and standard office media |
|
4. Maintenance |
Low. You need to make only ribbon replacements |
Moderate. You need to manage toner, drum, and sometimes fuser replacements |
|
5. Ideal For |
Industrial labels, barcodes, wire markers, and asset tags requiring long-term readability |
Office printing, reports, forms, short-term labels needing speed + sharp text |
|
6. Output Type |
Durable, fade-resistant, long-lasting functional print output |
High-speed, high-volume printing with a clean, professional finish |
|
7. Cost Considerations |
Higher upfront cost but lower long-term running cost due to durability and affordable consumables |
Lower purchase cost but higher ongoing cost from toner, drum, and maintenance, especially in volume printing |
Which Printer Offers Better Label Durability?
When it comes to label durability thermal transfer printer has a great edge. Thermal transfer printers produce labels that are significantly more durable than those from a laser printer. This ensures that barcodes and important information remain readable for a long time.
For applications like shipping labels, product identification, or asset tracking, this resilience is essential. By using specific thermal ribbons, such as resin, you can create labels that withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments. Laser-printed labels, which use toner fused to the surface, are much more susceptible to fading and damage, making them a less reliable choice for long-term or demanding labeling tasks.
If you are still unsure which is the right printer for you, you can check out this guide 5 reasons you didn't get the printer you wanted which will help you arrive at the perfect printer for your needs.
What Are the Advantages of Thermal Transfer Printing Over Laser Printing?
Thermal transfer printing offers several clear advantages over laser printing, especially when long-lasting, industrial-grade labels are required. Here they are:
-
Print on more than just paper: Thermal transfer supports polyester, polypropylene, vinyl, and other synthetics for broader industrial interoperability.
-
Get labels that stay readable longer: Wax or resin ribbons produce images that resist fading, smudging, abrasion, and environmental exposure.
-
Reduce downtime with simpler mechanics: Thermal engines have fewer moving parts, which means less maintenance and fewer failures over time.
-
Avoid static-related print defects: Thermal transfer avoids the electrostatic issues that can disrupt toner adhesion in laser printers.
While laser technology is excellent for general office documents, thermal transfer is engineered for superior print longevity and reliability, making it the stronger choice for high-quality, high-duty labeling.
Where Can You Buy The Latest Thermal or Laser Printers?
At DuraFast, you’re not just buying a printer. You’re buying proven expertise and a partner that understands industrial labeling inside out. We carry the latest thermal transfer, laser, and color label printers from the world’s leading brands, and we don’t simply “sell boxes.” We help businesses choose the right device based on their real-world application, durability requirements, media type, regulatory needs, and production volume.
From enterprise-grade RFID printers to compact desktop units, DuraFast supplies the full ecosystem: printers, labels, ribbons, ink, toner, and accessories, backed by knowledgeable support, fast delivery, and competitive pricing. So whether you’re upgrading your fleet or building a new label workflow, DuraFast doesn’t just ship hardware; we help you set up a labeling system that performs.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between thermal transfer printers and laser printers can significantly influence your printing choices. Each type of printer has its unique strengths, whether it’s the superior label durability offered by thermal transfer printing or the speed and efficiency of laser printing. By evaluating your specific needs, including print quality, application, and cost considerations, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is more durable, thermal transfer or laser labels?
When it comes to thermal transfer vs laser label durability, there's a clear winner: thermal transfer labels. The process of melting a resin or wax ribbon onto the label creates a print that withstands chemicals, heat, and abrasion.
Is thermal transfer printing more expensive than laser printing?
In the clash between thermal transfer printing vs laser printing, cost consideration is one main differentiating factor. A thermal transfer printer often has a lower initial cost. A laser printer has a higher upfront price and requires more maintenance.
Can thermal transfer printers print color labels?
Yes, thermal transfer printing technologies can produce color prints. While most commonly used for black-and-white printing, you can achieve color by using a specific color ink ribbon in the printing process. This allows for color-coding or branding on your labels.
Which industries use thermal transfer printers the most?
Thermal transfer printers are most common in industries that require durable, long-lasting labels. This includes manufacturing for product and assembly line tracking, logistics for shipping labels and barcodes, and healthcare for patient identification and specimen labeling.
Can you use a laser printer for heat transfer?
A standard laser printer is not designed for the heat transfer process used for apparel or special items. Although a laser printer uses heat to fuse toner to paper, it is a different printing process. True heat transfer applications require special paper and equipment.
