What Should You Know About Data Center Cabling?
13th Feb 2026
Key Highlights
-
Data center cabling is critical to performance, reliability, and scalability
-
Structured cabling reduces downtime and simplifies maintenance
-
Following recognized standards improves safety and long-term efficiency
-
Good cable management supports airflow, cooling, and system health
-
The right tools and labeling systems make cabling easier to manage and audit
Behind every reliable data center is a cabling system that most people never see, but when it’s poorly designed, the impact is immediate. Tangled cables, unclear routing, and missing documentation can slow troubleshooting, restrict airflow, and increase the risk of outages during routine changes.
Data center cabling is not just about connecting equipment. It plays a direct role in network performance, cooling efficiency, scalability, and operational safety. A well-planned cabling infrastructure allows teams to maintain uptime, adapt to growth, and respond quickly when issues arise.
In this guide, we explain what data center cabling involves, why it matters, the standards and components you should know, best practices for cable management, common mistakes to avoid, and the tools that support clean, compliant, and future-ready data center environments.
What Is Data Center Cabling and Why Is It Important?
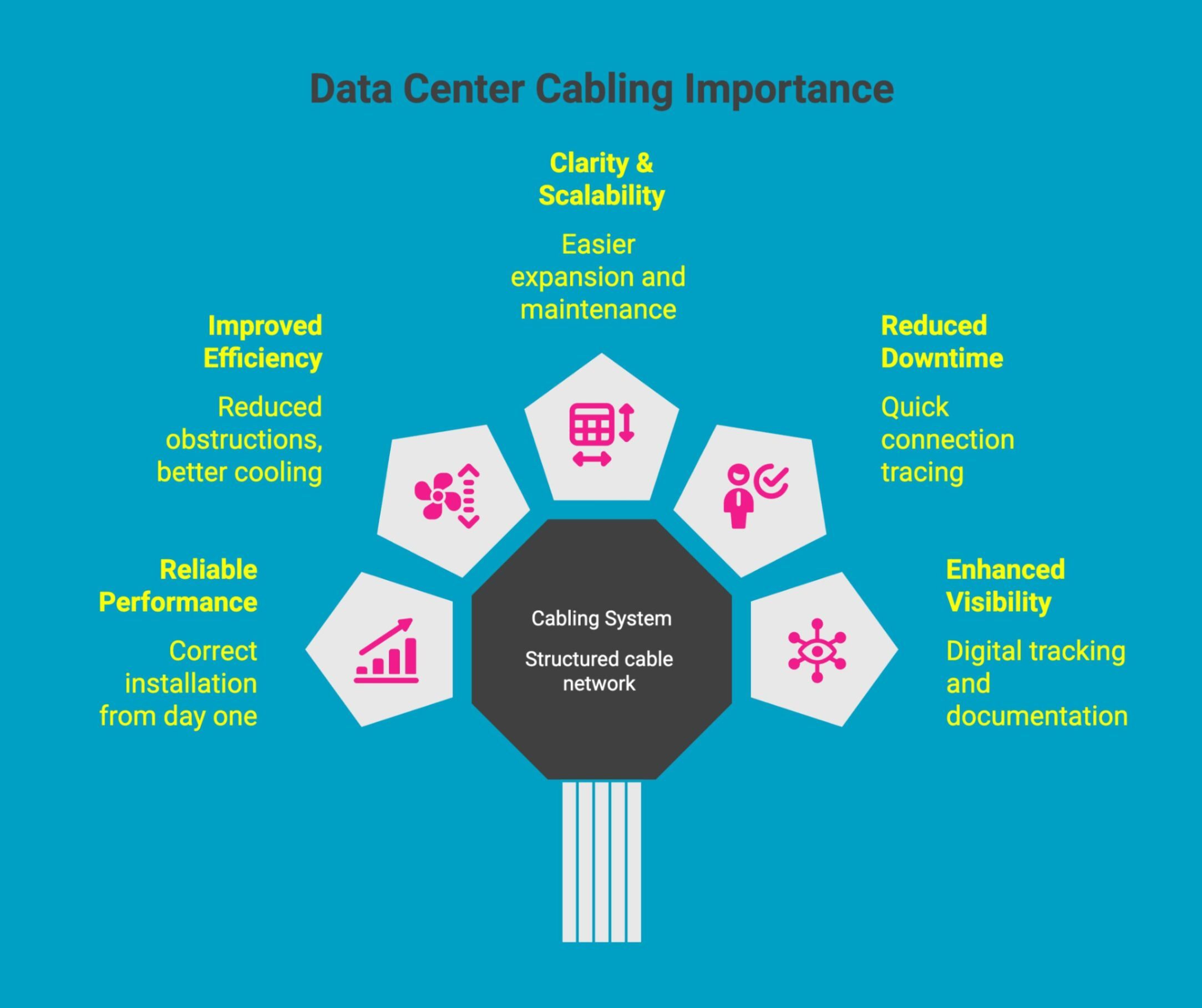
Data center cabling is the structured system of cables, pathways, connectors, and hardware that connects servers, storage, networking equipment, and power systems within a data center.
Why it matters:
-
Supports reliable performance during data center cable installation: Proper planning and structure ensure cables are installed correctly from day one, reducing errors, rework, and early performance issues that can affect network reliability.
-
Improves airflow and efficiency through data center cable management best practices: Organized cabling reduces obstructions, supports cooling efficiency, and helps prevent overheating in high-density racks and server environments.
-
Provides clarity and scalability with defined data center cabling structures: Standardized layouts make it easier to expand infrastructure, add equipment, and maintain consistency without disrupting existing operations.
-
Reduces downtime and troubleshooting time in cabling in data center environments: Clearly routed and labeled cables allow technicians to trace connections quickly, minimizing service interruptions and maintenance delays.
-
Enhances visibility and documentation with data center cable management software: Digital tools help track connections, changes, and layouts, keeping physical infrastructure aligned with documentation for audits, upgrades, and long-term management.
A well-designed cabling system is the foundation of a reliable data center, supporting performance, scalability, and efficient operations while reducing risk, downtime, and long-term maintenance challenges.
Want to choose the perfect color label printer for your business branding? Read this guide to learn how to pick the right color label printer that delivers professional results every time
What Are the Benefits of Proper Data Center Cabling?
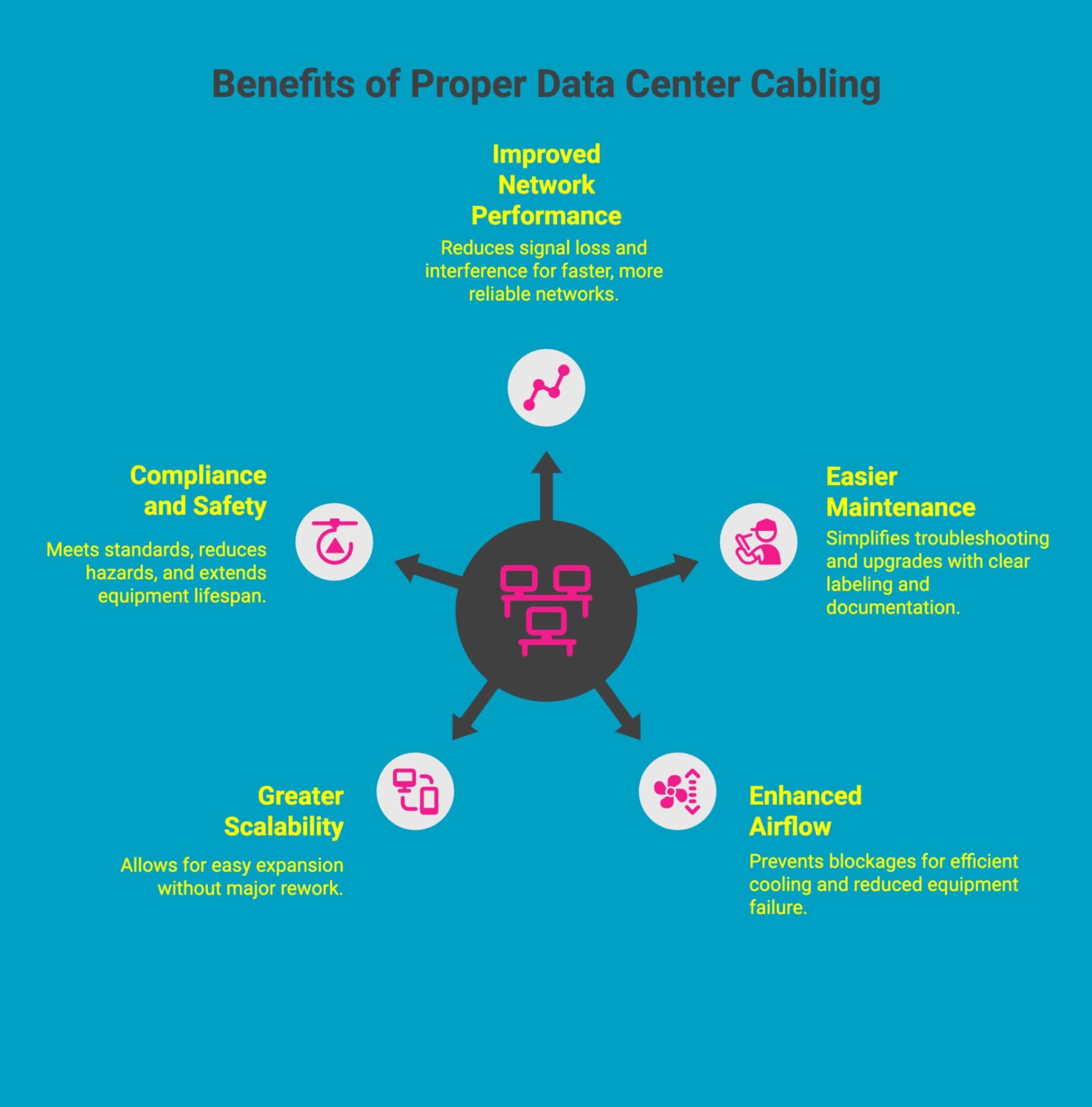
Proper data center cabling delivers far more than a neat appearance. A well-designed cabling system directly impacts performance, uptime, cooling efficiency, scalability, and operational cost control. When cabling is planned and maintained correctly, it becomes a strategic asset that supports reliability, growth, and long-term infrastructure stability.
These benefits are best understood across the following key areas:
1. Improved Network Performance and Reliability
Organized cabling reduces signal loss, electromagnetic interference, and accidental disconnections. By maintaining clean routing, correct cable types, and structured layouts, networks operate at optimal speeds with fewer errors, resulting in improved uptime, predictable performance, and reduced risk of unexpected outages.
2. Easier Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Upgrades
Clear cable paths, proper labeling, and consistent documentation allow technicians to quickly identify connections and isolate issues. This shortens troubleshooting time, minimizes human error during changes, and enables faster upgrades without disrupting adjacent systems or critical services.
3. Enhanced Airflow, Cooling, and Overall System Efficiency
Effective cable management prevents airflow blockages inside racks and aisles. By keeping cables properly routed and secured, cooling systems work more efficiently, temperatures remain stable, and the risk of heat-related equipment failure is significantly reduced.
4. Greater Scalability and Long-Term Cost Savings
Structured cabling makes it easier to expand capacity without major rework. New servers or network devices can be added using existing pathways and standards, reducing installation time, avoiding downtime, and lowering long-term operational and expansion costs.
5. Compliance With Safety Standards and Extended Equipment Lifespan
Standards-based cabling improves safety by reducing trip hazards, cable strain, and overheating risks. Proper installation helps equipment operate within design limits, extending lifespan and supporting compliance with safety, electrical, and infrastructure standards.
In summary, proper data center cabling improves performance today while protecting reliability, efficiency, and scalability for the future.
Looking to build an efficient labeling system across your entire business? This ultimate guide walks through strategies, tools, and best practices to create a labeling system that improves accuracy, organization, and productivity across every department.
What Are the Core Components of Data Center Structured Cabling?
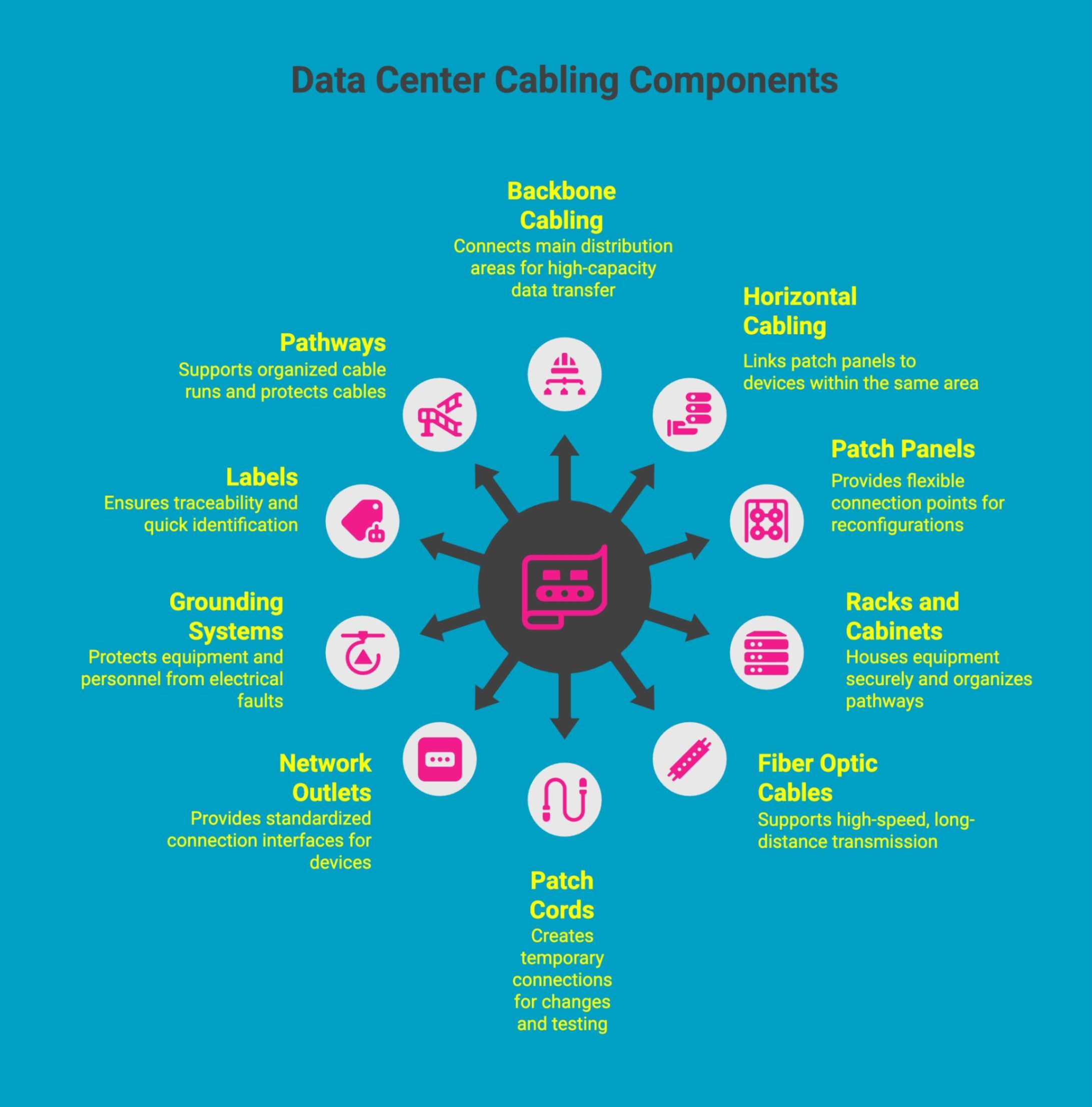
Data center structured cabling relies on a standardized framework of interconnected components designed to work together as one system. This approach improves organization, simplifies maintenance, supports scalability, and ensures reliable connectivity across servers, storage, networking equipment, and supporting infrastructure.
-
Backbone cabling (vertical infrastructure): Backbone cabling forms the core of the data center network, connecting main distribution areas, equipment rooms, and floors to support high-capacity data transfer and reliable communication across the entire facility.
-
Horizontal cabling: Horizontal cabling links patch panels to servers, switches, and other devices within the same area, ensuring consistent connectivity while supporting standardized layouts and easier troubleshooting.
-
Patch panels and cross-connect systems: These components provide flexible connection points that allow circuits to be reconfigured without disturbing permanent cabling, improving scalability and simplifying maintenance tasks.
-
Racks, cabinets, and cable management hardware: Racks and cabinets house equipment securely, while cable managers organize pathways, reduce strain, improve airflow, and maintain a clean, accessible infrastructure.
-
Fiber optic and copper cables: Fiber supports high-speed, long-distance transmission, while copper handles shorter runs and legacy systems, allowing data centers to balance performance, cost, and compatibility.
-
Patch cords and jumpers: Patch cords and jumpers create temporary or adjustable connections between equipment and panels, enabling fast changes, testing, and system upgrades.
-
Network outlets and termination points: These provide standardized connection interfaces for devices, ensuring reliable signal transfer and consistent installation across the data center environment.
-
Grounding and bonding systems: Proper grounding protects equipment and personnel by safely dissipating electrical faults, reducing interference, and supporting compliance with safety standards.
-
Labels and identification accessories: Clear labeling ensures traceability, supports accurate documentation, and allows technicians to identify connections quickly during installation, audits, or troubleshooting.
-
Pathways, conduits, and cable trays: These routing systems support organized cable runs, protect cables from damage, and make future expansion or maintenance more efficient and less disruptive.
Each component contributes to performance, safety, and maintainability.
What Data Center Cabling Standards Should You Follow?
Data center cabling standards provide a structured framework for designing, installing, and maintaining reliable infrastructure. Following recognized standards ensures consistency, safety, interoperability, and future compatibility, while reducing installation errors, simplifying maintenance, and supporting compliance across local and global data center environments.
The most important standards to follow include:
1. ANSI/TIA-568 Structured Cabling Standard
ANSI/TIA-568 defines general structured cabling requirements for commercial buildings and data centers. It covers cable types, performance categories, termination practices, and testing methods, helping ensure predictable network performance and consistent cabling design across different facilities.
2. ANSI/TIA-942 Data Center Infrastructure Standard
ANSI/TIA-942 focuses specifically on data center environments. It addresses cabling topology, redundancy levels, pathways, spaces, and layout considerations, making it essential for designing scalable, resilient, and well-organized data center cabling architectures.
3. ISO/IEC 11801 and ISO/IEC 24764 Global Cabling Standards
These international standards define structured cabling systems and data center-specific requirements for global deployments. They promote uniform design principles, performance benchmarks, and documentation practices, supporting consistency across multinational or multi-site data center operations.
4. NEC Article 645 and Local Electrical Codes
NEC Article 645 and local electrical codes regulate electrical safety, fire protection, grounding, and installation practices. Compliance ensures cabling systems meet legal safety requirements and reduces risks related to fire, electrical faults, and unsafe installations.
5. EN 50173 European Cabling Standard
EN 50173 governs structured cabling within European data centers and commercial buildings. It aligns with international standards while addressing regional requirements, ensuring interoperability, safety, and performance across European infrastructure projects.
Following these standards improves safety, simplifies expansion, and ensures long-term compatibility across evolving data center environments.
What Are the Best Practices for Data Center Cable Management?
Effective cable management is essential for maintaining reliable, efficient, and scalable data center operations. When cabling is properly organized and maintained, it supports performance, simplifies maintenance, improves airflow, and reduces the risk of outages or costly rework as infrastructure evolves.
The most effective data center cable management best practices include:
1. Plan Cable Pathways With Future Growth in Mind
Cable pathways should be designed to accommodate future expansion without overcrowding or redesign. Planning for growth ensures additional servers, switches, or storage can be added smoothly while maintaining accessibility, organization, and compliance with cabling standards.
2. Separate Power and Data Cables to Reduce Interference
Power and data cables should be routed separately to minimize electromagnetic interference and signal degradation. Proper separation improves network reliability, maintains data integrity, and reduces troubleshooting issues caused by noise or cross-interference.
3. Maintain Proper Cable Bend Radius and Routing Discipline
Following the manufacturer's bend radius guidelines prevents cable damage, signal loss, and premature failure. Structured routing discipline also improves consistency across racks and aisles, making maintenance safer, faster, and less prone to accidental disconnections.
4. Use Color-Coding, Labeling, and Documentation Consistently
Consistent color-coding and labeling allow technicians to identify cables quickly and accurately. When supported by up-to-date documentation, this approach reduces human error, speeds troubleshooting, and keeps physical infrastructure aligned with network records.
5. Perform Regular Audits to Optimize Airflow and Organization
Routine cabling audits help identify congestion, airflow blockages, and outdated routes. Regular maintenance ensures cooling efficiency remains high, cables stay organized, and potential issues are resolved before impacting performance or uptime.
Good cable management transforms cabling from a hidden risk into a reliable foundation for long-term data center performance.
Want to ensure wire labels stay clear and readable in complex data center environments? This guide explains how to do wire printing the right way, covering best practices, tools, and materials that help speed up installation
How Do You Plan and Install Data Center Cabling Properly?
Proper data center cabling is the result of careful planning, not last-minute installation decisions. Aligning cabling design with industry standards ensures the network infrastructure supports performance, scalability, and reliability while minimizing downtime, rework, and long-term operational constraints as the data center grows.
A successful cabling approach follows these key steps:
1. Conduct Site Assessments and Capacity Planning
Begin by evaluating physical space, power availability, cooling capacity, and future growth needs. Accurate assessments help determine cabling density, pathways, and expansion limits, ensuring the infrastructure can support higher bandwidth demands without congestion or redesign later.
2. Design Scalable Architecture Aligned With ANSI/TIA-942
Use ANSI/TIA-942 guidance from the Telecommunications Industry Association to design structured, scalable cabling layouts. This approach supports redundancy, efficient routing, and predictable performance across data halls, rows, and racks.
3. Select Appropriate Cable Types, Pathways, and Hardware
Choose fiber for long distances and high-speed links, and copper for short distances or shorter distances within racks. Selecting the right cable types and pathways ensures performance, durability, and compatibility with current and future equipment.
4. Implement Structured Cabling With Proper Labeling and Records
Install cabling using structured methods with consistent labeling and documentation. Clear records make it easier to manage changes, support audits, and maintain visibility across the entire network infrastructure.
5. Test, Certify, and Validate Performance Before Go-Live
Before activating systems, test and certify all cabling to confirm performance, continuity, and compliance. Validation ensures the installation meets design expectations and operates reliably under real-world workloads.
Thorough planning and disciplined installation reduce errors, limit downtime, and create a future-ready data center cabling foundation.
What Are the Common Mistakes to Avoid in Data Center Cabling?
Avoiding these common cabling mistakes lays the groundwork for a more reliable and efficient data center. With proper routing, separation, quality materials, and clear labeling, teams can reduce downtime, simplify maintenance, and create a scalable infrastructure that supports long-term growth and performance.
-
Overcrowding pathways and ignoring routing discipline: Overfilled trays and unmanaged routes make cables difficult to trace, increase physical stress, and raise the risk of damage during maintenance or future expansion.
-
Mixing power and data cables without separation: Running power and data together can introduce electrical interference, degrade signal quality, and create safety concerns that impact network performance and compliance.
-
Using incorrect cable lengths or low-quality materials: Excessively long cables add clutter and restrict airflow, while poor-quality materials increase failure rates and reduce overall system reliability.
-
Skipping labeling, documentation, and identification: Missing or inconsistent labels make troubleshooting slow and error-prone, leading to longer downtime and higher operational risk during changes or audits.
-
Neglecting airflow and cooling considerations: Poor cabling layout can block airflow, causing heat buildup that stresses equipment and increases the likelihood of performance issues or hardware failure.
Avoiding these errors improves reliability, scalability, and overall operational efficiency within the data center.
What Tools and Software Support Data Center Cable Management?
Effective data center cable management depends on using the right combination of physical tools and software. These solutions help teams plan installations, maintain organization, verify performance, and track changes over time, reducing errors, improving visibility, and supporting reliable, scalable data center operations.
-
Cable testers, certifiers, and network analyzers: These tools verify cable performance, detect faults, measure signal quality, and ensure installations meet required standards before systems go live or after changes are made.
-
Label printers and identification systems: Professional labeling tools create clear, durable identifiers for cables, patch panels, and ports, improving traceability, speeding up troubleshooting, and keeping documentation aligned with physical infrastructure.
-
Rack and cabinet management tools: Physical management accessories help organize cables within racks, reduce strain, improve airflow, and maintain clean layouts that simplify access during maintenance or upgrades.
-
DCIM software for real-time monitoring: Data Center Infrastructure Management software provides visibility into connections, capacity, power, and changes, helping teams track assets, plan growth, and reduce operational risk.
-
CAD and cable design software: Design tools support accurate planning of cable routes, layouts, and pathways, allowing teams to model installations, avoid congestion, and document infrastructure before and after deployment.
These tools support accuracy, visibility, and long-term control across complex data center environments.
How Can the MAX LETATWIN LM-550A3BH Printer Improve Data Center Cabling?

In data center environments, unclear or inconsistent cabling labels create major pain points, slower troubleshooting, higher risk of errors, failed audits, and costly downtime when teams can’t quickly trace connections. The MAX LETATWIN LM-550A3BH solves this by producing clear, durable labels that stay readable in dense, high-traffic racks and harsh conditions.
With DuraFast Label Company, organizations get more than a printer: they get expert guidance, reliable supplies, and easy access to professional labeling solutions that help keep documentation aligned with physical infrastructure and operations running efficiently.
Contact us today for all your data center labeling needs, from the MAX LETATWIN LM-550A3BH to professional guidance on building a cleaner, more efficient, and compliant cabling system.
Conclusion
Data center cabling is foundational to performance, reliability, and scalability. By following recognized standards, using structured cabling components, maintaining disciplined cable management, and investing in proper tools and labeling, organizations can reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and future-proof their data center infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common types of cables used in data center cabling?
Data centers commonly use fiber optic cables for high-speed backbone links and copper Cat6 or Cat6A cables for horizontal connections within racks alongside data center power cables supporting reliable electrical distribution and equipment operation across modern facilities.
What are the key standards for data center cabling?
Key data center cabling standards include ANSI/TIA-568 and ANSI/TIA-942, with ISO/IEC frameworks defining structured layouts, safety, and performance alongside NEC requirements, while data center power cables follow electrical codes, ensuring compliant infrastructure for modern mission-critical facilities operations.
How is structured cabling implemented in data centers?
Structured cabling in data centers uses standardized pathways, patch panels, labeling, and documentation to create organized, scalable systems supporting predictable performance, easier maintenance, and separation of network links from data center power cables infrastructure within controlled environments facilities.
What is the difference between top-of-rack and end-of-row cabling architectures?
Top-of-rack cabling places switches inside each rack, reducing cable lengths, while end-of-row centralizes switching at row ends, increasing run distances and coordination with data center power cables, planning for airflow scalability and maintenance efficiency.
How do you plan the layout for cabling in a data center?
Planning data center cabling layouts requires capacity assessment, pathway design standards selection, cooling considerations, and detailed documentation while coordinating network routes with data center power cables to support scalability, safety, and future expansion across evolving facility requirements environments.
Why is cable management important in data center environments?
Cable management is critical because it improves airflow, reduces downtime, simplifies troubleshooting, and prevents accidental disconnections, overheating, and interference while clearly separating network connections from data center power cables to maintain reliability, safety compliance, and operational efficiency standards.
What are the main challenges with data center cabling, and how can they be solved?
Common data center cabling challenges include congestion, poor documentation, limited scalability, and human error, solved through structured design, consistent labeling, regular audits, and aligning network pathways with data center power cables, planning to improve reliability, safety, and expansion.
Which tools are commonly used for testing and verifying data center cabling?
Testing data center cabling relies on cable certifiers, network analyzers, fiber testers, and continuity tools to validate performance standards and compatibility while ensuring separation and safety around data center power cables during installation, upgrades, audits, and troubleshooting activities.
How often should data center cabling be inspected or upgraded?
Data center cabling should be inspected regularly and reviewed during equipment changes or performance issues, with upgrades planned as bandwidth grows, while coordinating updates to data center power cable systems for term reliability compliance and capacity planning.
